UX Research and Design
UXR
This project explores the integration of AI into Agile UX design workflows to streamline processes, enhance creativity, and improve efficiency. Through extensive research, design, and testing, the project addresses challenges like aligning user research with sprint timelines, maintaining design standards, and assisting designers without replacing human creativity. The outcome includes a structured design system, AI-driven use cases, and refined prototypes that enable designers to work smarter and faster while ensuring user-centric solutions.
Problem Statement
Good UX design enhances functionality and usability, enabling users to achieve their goals while supporting business growth. In contrast, poor UX results in user frustration, reduced engagement, and misuse of services. To address this, designers must align the overall user experience with end-user requirements and expectations by adopting iterative, user-centered approaches grounded in research and problem-solving.
However, designing user-friendly solutions is inherently complex, time-intensive, and resource-heavy. Designers face the dual challenge of understanding what to create (problem-setting) and how to create it (problem-solving), often in the absence of sufficient user interaction data, which exacerbates these complexities.
To address these challenges, I conducted extensive research on existing literature around AI-driven UX and traditional UX frameworks. This exploration uncovered key challenges, innovations, and benefits within various design methodologies. These insights form the foundation for developing improved AI-integrated UX design processes and practical use cases.

The literature review revealed gaps in AI integration in UX design process, leading to the central research question:
How does AI integration affect designers' efficiency, creativity, and overall experience?
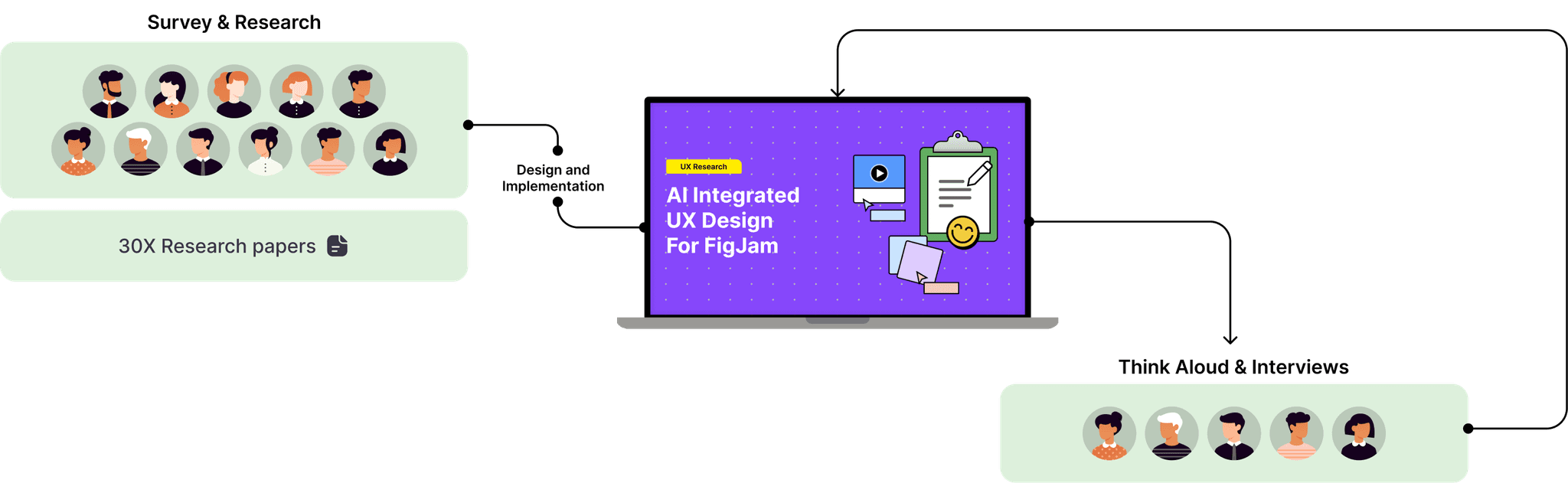
Design and Implementation
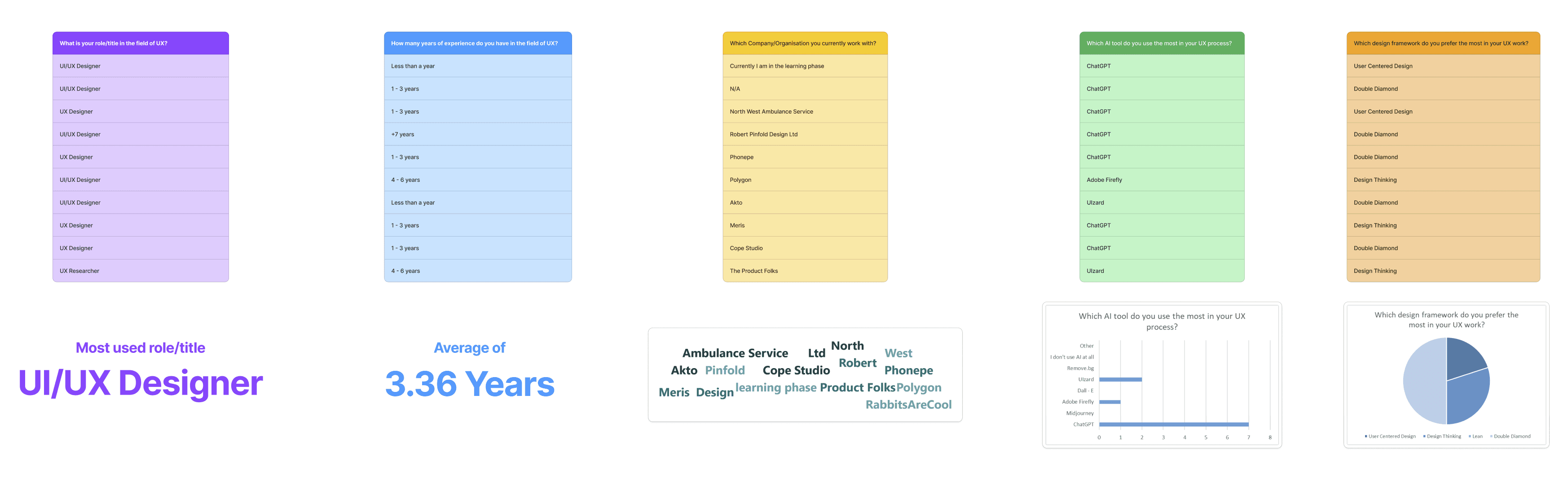
After conducting the survey with 11 UX professionals to understand current practices and challenges in UX design. The data gathered were analysed using thematic analysis for qualitative data and charts for quantitative data.
Thematic Analysis
Key themes identified include:
Enhanced Efficiency: AI tools improve productivity by automating tasks.
Boosts Creativity: AI aids in idea generation and creative processes.
Variety of AI Tools: Different AI tools support various design stages.
Experiences and Challenges: Issues with creativity, accuracy, and usability of AI tools.
Quantitative Analysis: Close-ended questions provided insights into roles, experience, AI tools used, and preferred design frameworks. ChatGPT was the most utilized AI tool, with 70% of respondents favoring it.
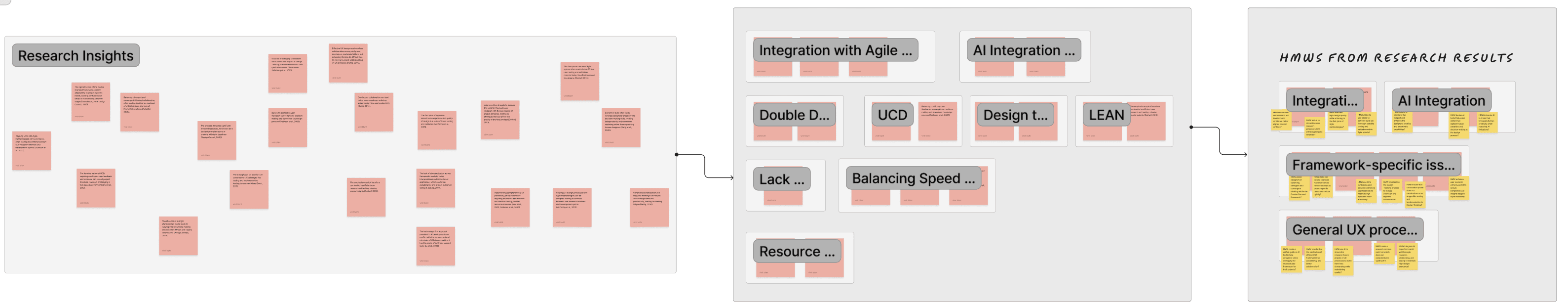
HMWs (How Might We)
Through my research, I identified key challenges in UX design frameworks, including lack of standardization, resource and time constraints, and difficulty balancing speed with quality. To address these, I coded insights to generate themes and crafted "How Might We" (HMW) questions to frame the challenges:
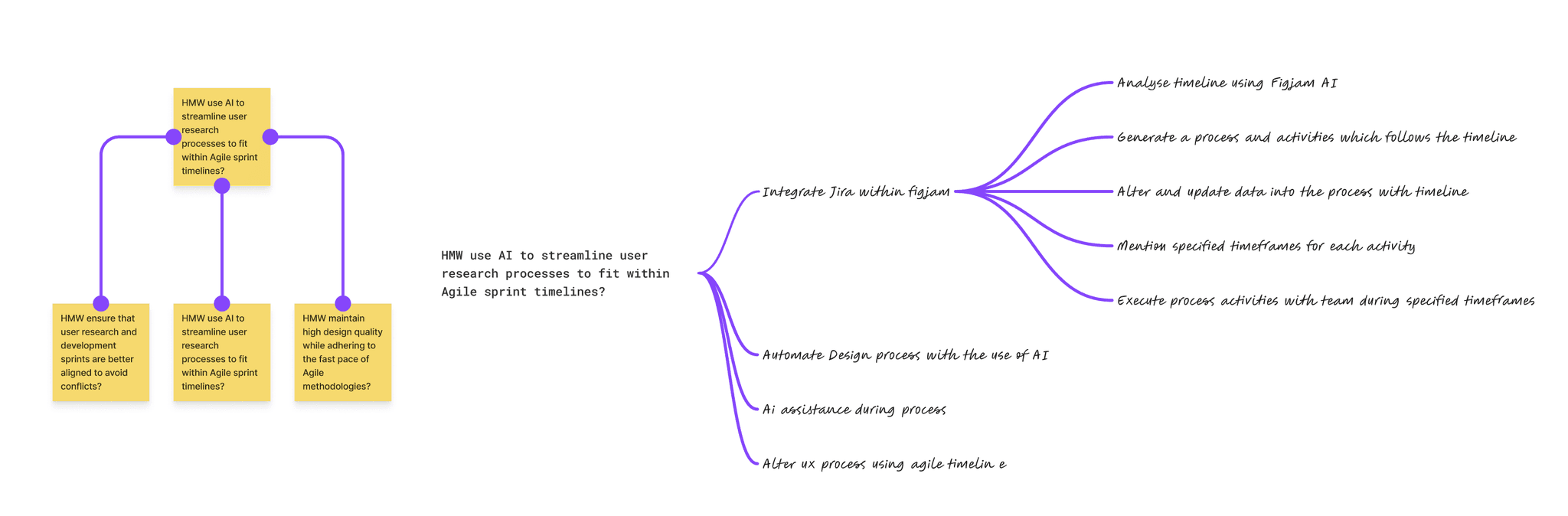
HMW use AI to streamline user research processes within Agile timelines?
HMW integrate AI for rapid yet thorough research, prototyping, and testing while maintaining quality?
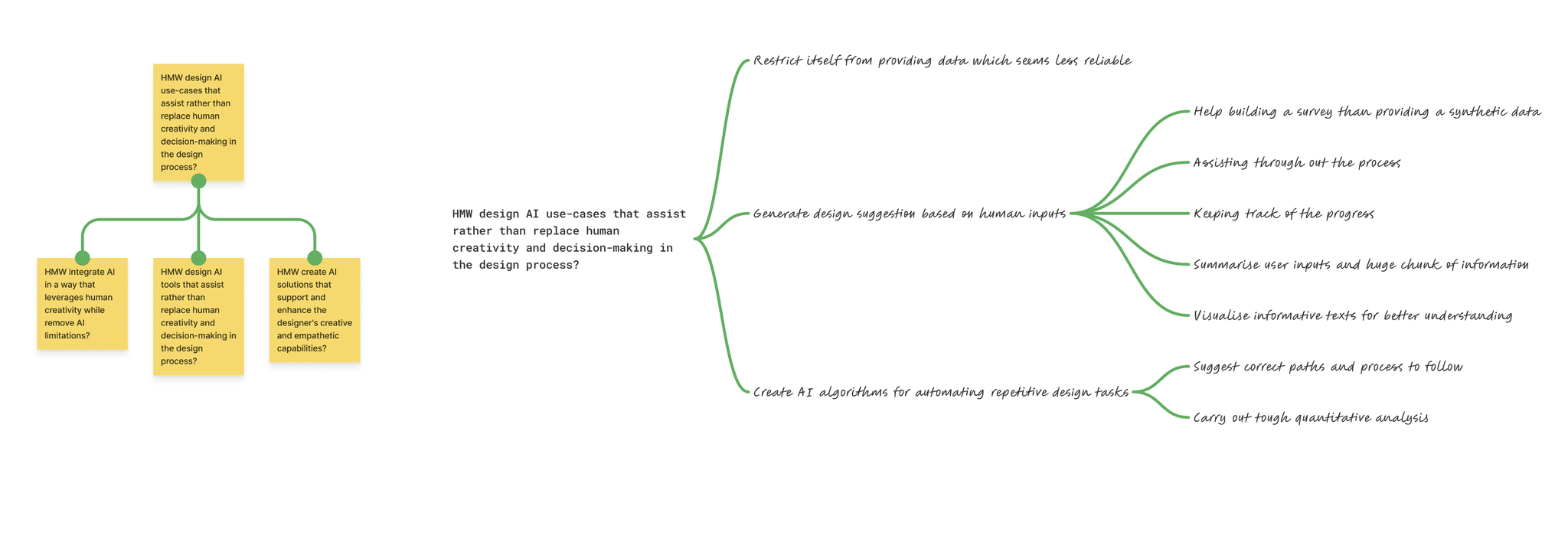
HMW design AI use-cases that enhance rather than replace human creativity in design?
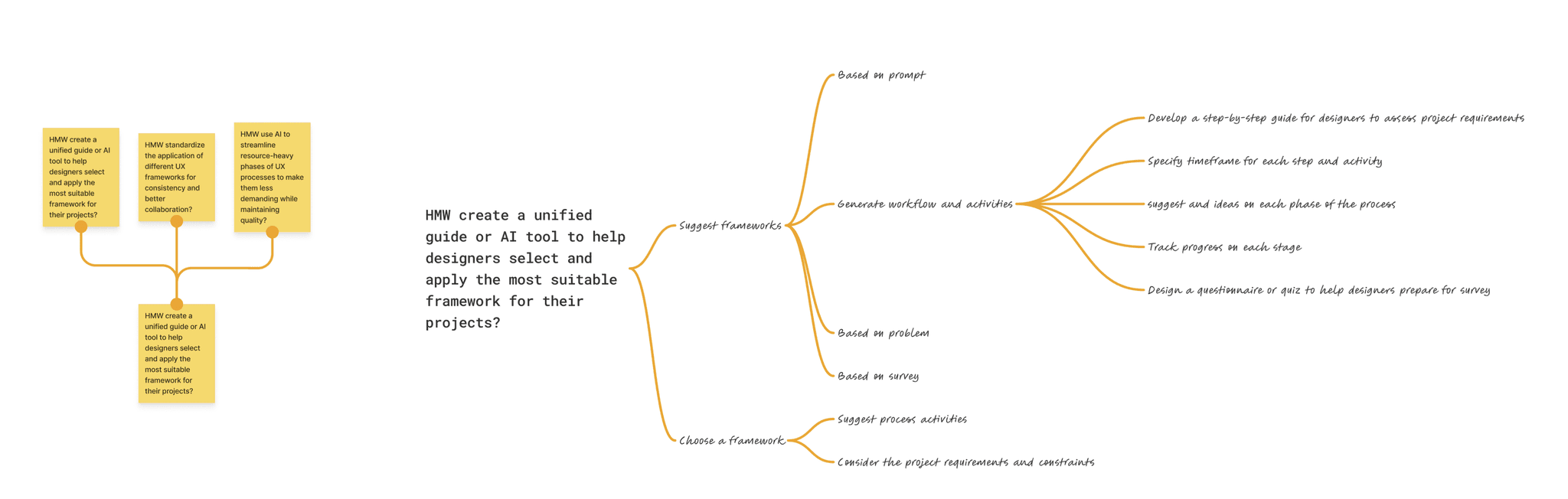
HMW create an AI tool to guide designers in selecting the best framework for their projects?
These HMWs transformed broad challenges into actionable problem statements, paving the way for innovative AI-integrated UX solutions.
Mind Mapping
The mind map was used to organize and explore "How Might We" (HMW) questions, focusing on integrating AI to enhance various aspects of the UX design process. By mapping these questions, I identified key challenges and potential AI-driven solutions, breaking down complex problems into manageable themes. This approach provided clarity and a structured pathway for addressing the challenges, enabling me to visualize connections and refine my problem-solving strategies effectively.
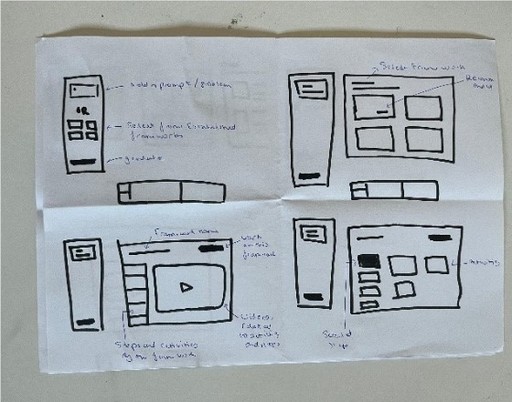
Crazy 8s
Using the Crazy 8s technique, ideas from the mind map were sketched within 8 minutes, focusing on screen structures starting with a user prompt and ending with research outputs. One HMW question, like "How might AI streamline user research in Agile sprints?" guided the process to keep concepts targeted and relevant.
This quick, spontaneous exercise generated diverse visuals and set the foundation for the user flow, developed afterward.
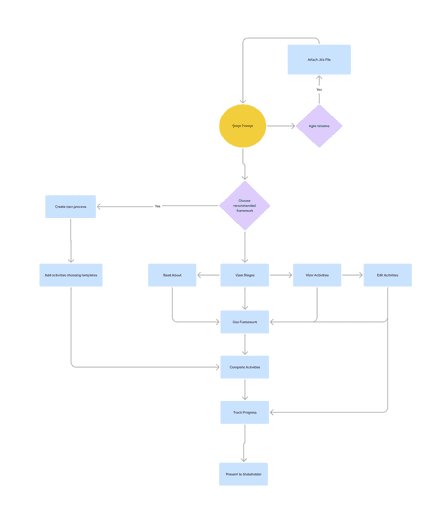
User Flow
The user flow diagram was created to map out the most efficient path for users, reducing friction and optimizing their experience. It clarified how AI could be integrated into Agile UX design by defining key steps like inputting queries, aligning with Agile timelines, selecting or customizing frameworks, and tracking progress in real-time.
This process highlighted opportunities to streamline workflows, ensure flexibility, and maintain control over design stages. It also emphasized clear documentation and reporting to enhance communication with stakeholders. The diagram helped identify potential bottlenecks and ensured a seamless, user-focused design journey.
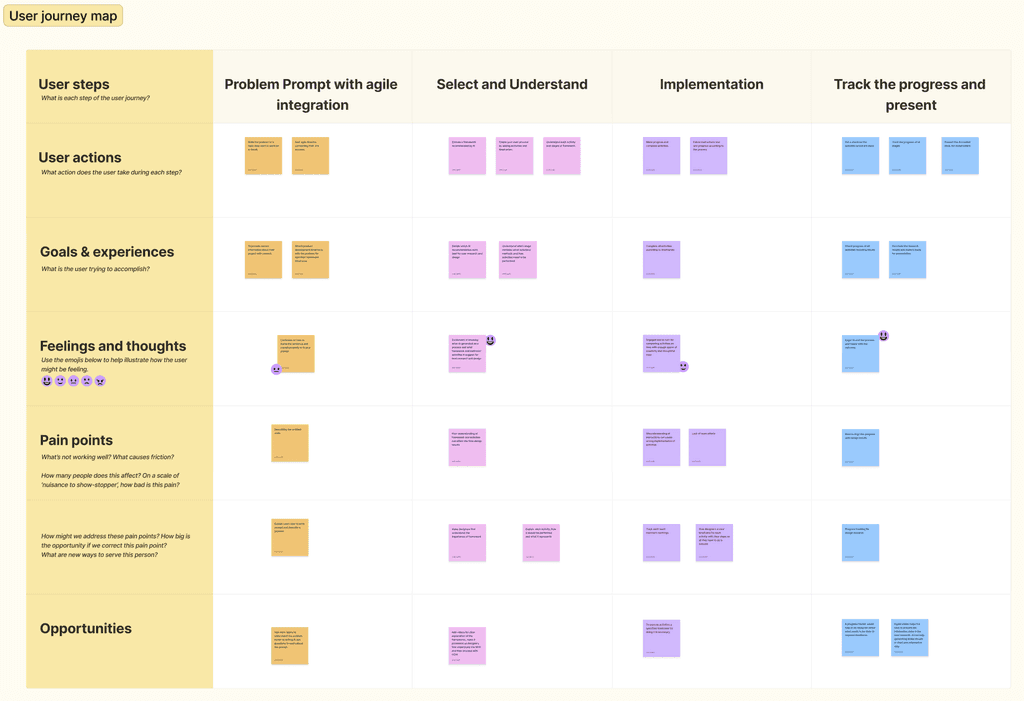
User Journey Mapping
The journey map was used to outline the UX designer’s process, from identifying problems to implementing solutions and monitoring outcomes. It highlighted challenges in aligning Agile methodologies with user research and showed how AI recommendations simplify complex decisions, like selecting frameworks and activities.
It revealed the need for flexibility during implementation, frequent modifications to meet user requirements, and effective communication with stakeholders. The map provided clarity on pain points, user experiences, and opportunities to create more user-centric solutions through AI support.
Challenges and Solutions
Streamlining User Research
Challenge: Aligning user research with Agile sprints.
Solution: Integrated Jira with FigJam for sprint-aligned processes, using AI for automated updates and real-time adjustments.
Maintaining Design Standards
Challenge: Conducting research, prototyping, and testing quickly without losing quality.
Solution: Defined clear timelines, used AI tools like UIzard for rapid prototyping, and applied machine learning to analyze user data.
Supporting Designer Creativity
Challenge: Ensuring AI enhances rather than replaces creativity.
Solution: Created AI use-cases to automate repetitive tasks, provide data-driven suggestions, and support designers’ creative work.
Framework Selection
Challenge: Helping designers choose the right frameworks.
Solution: Developed an AI tool offering tailored framework recommendations to fit project needs.

Hi-Fi Wireframes (Visualising Interfaces)
Wireframes and Hi-fi designs were created to translate insights and frameworks from earlier phases into functional visuals.
Wireframes: Focused on layout, spacing, and positioning of key components, serving as the foundation for detailed designs.
Hi-fi Designs: Refined the wireframes by adding visual styles, specific icons (e.g., a progress tracker), tables, and usability-enhancing elements.